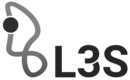control_applications
-
Temperature controlled retinal laser treatmentLed by: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Matthias MüllerTeam:Year: 2020Funding: Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) - 430154635Duration: 2020 - 2021
-
Multi-vehicle trajectory planning using MPCLed by: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Matthias MüllerTeam:Year: 2021Funding: Industrial ProjectDuration: 2021 - 2025
-
Cont4Med - Estimation and control under limited information with application to biomedical systemsLed by: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Matthias MüllerTeam:Year: 2021Funding: This project has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (grant agreement No 948679).Duration: 2021 - 2025
![]()
![]()
-
roboterfabrikLed by: Matthias Müller, Thomas Seel, Torsten LilgeTeam:Year: 2023Funding: Region HannoverDuration: 2023-2025
![roboterfabrik]()
![roboterfabrik]()
learning_and_data_based
-
Cont4Med - Estimation and control under limited information with application to biomedical systemsLed by: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Matthias MüllerTeam:Year: 2021Funding: This project has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (grant agreement No 948679).Duration: 2021 - 2025
![]()
![]()
-
Convex online optimization for dynamic systems controlLed by: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Matthias MüllerTeam:Year: 2023Funding: Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) - 505182457Duration: 2023 - 2025
model_predictive_control
-
Robust and stochastic economic model predictive controlLed by: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Matthias MüllerTeam:Year: 2020Funding: Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) - 279734922Duration: 2020 - 2023
-
Multi-vehicle trajectory planning using MPCLed by: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Matthias MüllerTeam:Year: 2021Funding: Industrial ProjectDuration: 2021 - 2025
nonlinear_estimation_and_control
-
Robust stability and suboptimality in nonlinear moving horizon estimation - From conceptual to practically relevant guaranteesLed by: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Matthias MüllerTeam:Year: 2020Funding: Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) - 426459964Duration: 2020 - 2026
-
Cont4Med - Estimation and control under limited information with application to biomedical systemsLed by: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Matthias MüllerTeam:Year: 2021Funding: This project has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (grant agreement No 948679).Duration: 2021 - 2025
![]()
![]()
[uncategorized]
-
Inertiale MesseinheitZweibeinige Roboter benötigen zur Gleichgewichtsregelung einen Sensor, der ähnlich dem Gleichgewichtsorgan des Menschen die Orientierung im Raum erfassen kann. Die in der Trägheitsnavigation üblichen Sensorsysteme sind für diese Aufgabe wegen des zu hohen Gewichts und zu hoher Stromaufnahme ungeeignet. Mit der rasanten Entwicklung mikromechanischer Sensoren haben sich kostengünstige Alternativen ergeben, die jedoch wesentlich größere Messfehler aufweisen. Im Rahmen des Projektes wurde eine leichte Sensoreinheit mit geringem Stromverbrauch entwickelt, deren Fehler sich durch redundante Messungen und intelligente Datenfusion auf ein für die Anwendung gerechtes Maß reduzieren lassen.Led by: Prof. Dr.-Ing. W. GerthTeam:Year: 2005Funding: MZH-InnovationsprojektDuration: 2000-2005
![]()
![]()
-
Detection, Classification and Prevention of Impending Falls of Bipedal RobotsThe bipedal locomotion allows service robots to move within the human environment with highest possible flexibility, but also leads to difficult stabilization and a high probability of falling down. Common stability criteria are not sufficient for the detedtion and classification of impending falls. In this project, methods for detection and classification of impending falls are derived together with learning of optimal reactions. Finally, approaches for standing up after a fall were evaluated.Led by: Prof. Dr.-Ing. W. GerthTeam:Year: 2008Funding: DFGDuration: 2003-2008
![]()
![]()
-
Zweibeiniger autonomer Serviceroboter LISALISA ist ein Versuchsroboter für die Weiterentwicklung und Erprobung neuer Verfahren für zweibeinige Laufmaschinen. Eine Besonderheit dieser Laufmaschine ist die kugelgelenkähnliche Konstruktion der Hüftgelenke. Die beiden Beine des Roboters sind derart beweglich, dass jeder Fuß in alle drei Raumrichtungen verschiebbar und um jede Raumachse drehbar ist.Led by: Prof. Dr.-Ing. W. GerthTeam:Year: 2009Duration: 2002-2009
![]()
![]()
-
Zweibeiniger Serviceroboter BARtFür autonome Serviceroboter sind einerseits Radantriebe sehr effizient. Für zahlreiche Anwendungen im menschlichen Lebensraum bestehend aus Treppen und anderen Hindernissen, die nicht von Rädern bewältigt werden können, erscheint ein Beinantrieb vorteilhafter. Zur Untersuchung des dynamischen Gehens wurde der zweibeinige Roboter BARt-UH (Bipedal Autonomous Robo-Universität Hannover) aufgebaut. Die Experimentierplattform BARt findet in überarbeiteter Form bis heute in weiteren Forschungsprojekten Anwendung.Led by: Prof. Dr.-Ing W. GerthYear: 2012Duration: 1999-2012
![]()
![]()
-
"3rd Arm" - Craftsmen-Force-Assistence with adaptive Human-Machine InteractionRegarding an aging work force with higher requirements for work efficiency, a force assistence system is developed. The system is based on a mechatronic structure ("3rd arm"), which is fixed to the body of the user via a supporting construction. Apart from the physical support the system meets cognitive assistance functions. Thus, it provides force support on the one hand and on the other hand the increase in work efficiency and quality of work.Team:Year: 2014Funding: Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF)Duration: 3 Jahre
![]()
![]()
-
Robot FactoryThe "Robot Factory" ("Roboterfabrik") is project funded by the Region Hannover, which is aiming for a leading role of Hannover in the education in robotics and in the schooling of the new generation of "Robotic Natives" within the areas of engineering and computer sciences. Therefore, the "Robot Factory" is the first and central element for Hannover towards a leading robotic site.Year: 2016Funding: Region HannoverDuration: 2016-2020
-
SoftPro: Synergy-based Open-source Foundations and Technologies for Prosthetics and RehabilitatiOnSoftPro project will study and design soft synergy-based robotics technologies to develop new prostheses, exoskeletons, and assistive devices for upper limb rehabilitation, which will greatly enhance the efficacy and accessibility to a greater number of users. Building on solid methodological bases, SoftPro will produce a significant social impact, promoting advanced robot prosthetic and assistive technology “from bench to bedside”; but it will also introduce disruptively new, admittedly risky but potentially high-impact ideas and paradigms. This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 688857Led by: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Sami HaddadinYear: 2016Funding: EU, H2020Duration: 4 Jahre
-
MobIPaRThe aim of the project is to refine an existing verticalizable nursing- and rehabilitation bed, that is linked with a robotic-supported gait-therapy, in such a way that it becomes auto-adaptive. This way, even non-trained personnel may operate the device in an intuitive way.Led by: Prof. Dr.-Ing Sami HaddadinYear: 2017Funding: Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF)Duration: 3 Jahre
![]()
![]()
-
ILIAD: Intra-Logistics with Integrated Automatic DeploymentToday, intralogistic services have to respond quickly to changing market needs, unforeseeable trends and shorter product life cycles. These drivers pose new demands on intralogistic systems to be highly flexible, rock-solid reliable, self-optimising, quickly deployable and safe yet efficient in environments shared with humans. ILIAD will enable the transition to automation of intralogistic services with key stakeholders from the food distribution sector, where these challenges are particularly pressing. This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 732737Led by: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Sami HaddadinYear: 2017Funding: EU, H2020Duration: 4 Jahre